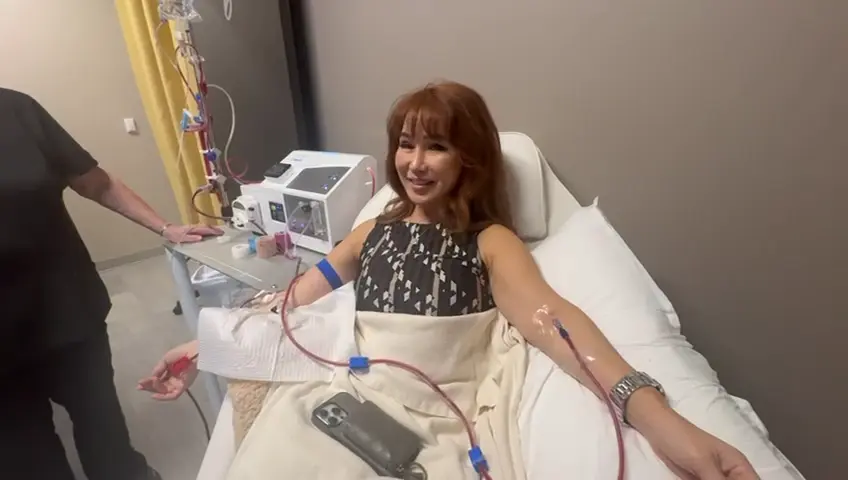
Ozone therapy has garnered attention in recent years for its potential health benefits, including immune boosting, detoxification, and inflammation reduction. However, there are many different methods of delivering ozone into the body, which can be confusing for those new to this type of treatment. In this article, we’ll break down the various methods of ozone …
EBOO Ozone therapy has garnered attention in recent years for its potential health benefits, including immune boosting, detoxification, and inflammation reduction. However, there are many different methods of delivering ozone into the body, which can be confusing for those new to this type of treatment. In this article, we’ll break down the various methods of ozone therapy, answer common questions, and provide helpful insights into its uses, effectiveness, and cost.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional before undergoing any treatment.
1. The Difference Between Insufflations, EBOO & HD IV Ozone & 10 Pass
When it comes to EBOO ozone therapy, there are several delivery methods, each with its own benefits and applications. Let’s break them down:
Insufflations
Ozone insufflations involve introducing ozone gas into the body through different entry points, including the rectum, vagina, ear, or nostrils. This method helps deliver ozone directly to the area of concern, such as digestive or respiratory issues, and can be an effective option for people who prefer a non-invasive method.
EBOO Ozone Therapy & HD IV Ozone
EBOO (Extracorporeal Blood Oxygenation and Ozonation) is a medical procedure that involves drawing blood from the body, mixing it with ozone, and then returning it to the bloodstream. HD (High-Dose) IV ozone therapy is similar but focuses on delivering a higher concentration of ozone directly into the bloodstream via an intravenous drip. EBOO Ozone Therapy is often preferred over the traditional 10-pass ozone therapy due to its ability to address more systemic issues, such as chronic illness and inflammation, in a more controlled and efficient way.
10 Pass Ozone
The 10-pass ozone method involves drawing blood out of the body, ozonating it, and then returning it in multiple “passes” (typically 10). While this method can be effective, it is older and less precise compared to EBOO, which is considered a more advanced and efficient option. EBOO allows for better control of the ozone dosage and can be adjusted to meet the individual’s specific needs. For most people, EBOO or HD IV ozone therapy is considered a better alternative to the 10-pass method.
2. Can Children Benefit from Ozone Insufflations?
While ozone therapy is generally safe for adults, the use of ozone in children should be approached with caution. Ozone insufflations can be beneficial for specific health issues, such as respiratory problems or immune system support, but it is crucial that ozone therapy for children is done under the supervision of a healthcare professional who is familiar with pediatric care. As a general rule, children’s bodies are more sensitive, and dosing needs to be more controlled.
3. Why Is Ozone Not Approved by the FDA?
EBOO Ozone therapy is not approved by the FDA because it is considered an alternative treatment, and there has not been enough large-scale clinical research to satisfy the agency’s requirements for approval. While ozone therapy has shown promising results in various studies, it has not yet been accepted as a mainstream treatment due to the need for more extensive data on its long-term effects and safety. That said, ozone therapy is widely used in other countries and is gaining more attention in the alternative medicine community.
4. Is EBOO Ozone Therapy Addictive?
No, ozone therapy is not addictive. Ozone does not have addictive properties like certain medications or substances. It works by enhancing oxygen delivery and promoting healing in the body. However, some people may feel the benefits of EBOO ozone therapy, such as improved energy or reduced pain, and may choose to continue treatments for ongoing health maintenance. This is not addiction, but rather an individual’s decision to continue the therapy for long-term benefits.
5. Do You Have to Be on Ozone for Life?
No, ozone therapy does not require lifelong treatment. Many individuals use ozone therapy for short-term health issues or during acute phases of illness to help accelerate recovery. Some people may choose to continue treatments periodically to maintain their health, boost their immune system, or manage chronic conditions. The frequency of treatments depends on individual health needs and goals, and it is up to the individual and their healthcare provider to determine the appropriate course of action.
6. What’s the Difference Between Ozone in the Air, Sanitizing Agent, and Medical Grade Ozone?
There are several types of ozone that are used for different purposes, and it’s important to understand the differences:
- Ozone in the Air: This is the ozone we encounter naturally in the atmosphere. While it can be beneficial in the upper atmosphere (protecting us from harmful UV rays), ozone near the ground can be harmful when inhaled. This is why ozone is often used as a pollutant indicator in environmental studies.
- Sanitizing Agent: Ozone is used as a powerful disinfectant in water treatment and air purification systems because of its ability to kill bacteria, viruses, and mold spores. This type of ozone is used in industrial and commercial applications.
- Medical Grade Ozone: This type of ozone is created for use in therapeutic settings. It is carefully controlled and administered in small, precise doses to help with a variety of medical conditions, including pain management, detoxification, and immune system support.
Medical grade ozone is much more controlled and purified compared to ozone used in industrial or environmental applications. It is delivered through specific methods, such as insufflations, IV infusions, or EBOO, to ensure its safety and effectiveness for therapeutic use.
7. Is Ozone a New Modality? Why Haven’t I Heard of It All My Life?
Ozone therapy is not exactly new—it has been used in medical practice since the early 20th century. However, it has remained somewhat under the radar in mainstream medicine due to its alternative nature and lack of widespread approval by regulatory agencies like the FDA. That being said, ozone therapy has been used successfully in various countries for decades and is now gaining more attention in the United States and other parts of the world. As alternative medicine becomes more popular and people seek out natural healing options, ozone therapy is starting to be recognized as a viable treatment for a wide range of health concerns.
8. How Much Does EBOO Ozone Therapy Treatment Cost?
The cost of ozone therapy can vary depending on the method of delivery and the clinic you visit. Typically, prices range from $100 to $300 per session for standard ozone treatments like IV ozone or insufflations. More advanced treatments like EBOO therapy can cost more, with sessions ranging from $1,000 to $2,500 or more. It’s important to check with your healthcare provider or clinic for specific pricing, as costs can vary based on location and treatment type.
9. How Do You Feel After an Ozone Treatment?
Most people report feeling energized, refreshed, and more alert after an ozone treatment. The therapy is designed to enhance oxygen delivery to tissues, which can help reduce inflammation, improve circulation, and support the body’s natural detoxification processes. Some individuals may experience mild side effects such as fatigue or slight dizziness after their first session, but these typically subside quickly. As with any treatment, responses vary from person to person.
10. What Is EBOO Treatment?
EBOO (Extracorporeal Blood Oxygenation and Ozonation) is a process in which blood is drawn from the body, ozonated (exposed to ozone), and then returned to the body. This method provides a more powerful and effective way to deliver ozone throughout the system, supporting immune function, reducing inflammation, and promoting overall health. EBOO Ozone Therapy is often used for more severe or systemic conditions and is considered a more advanced method than traditional ozone therapies.
Frequently Asked Questions about EBOO Ozone Therapy
How Many Sessions of Ozone Therapy Do I Need?
The number of sessions needed depends on the individual and the condition being treated. Some people see results after just one session, while others may need multiple treatments over the course of several weeks or months. It’s important to follow the guidance of your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate treatment plan.
Is EBOO Ozone Therapy Covered by Insurance?
Currently, ozone therapy is generally not covered by insurance, as it is considered an alternative treatment. However, this may change as more research is conducted and more clinical evidence is gathered. Always check with your insurance provider for specifics regarding your policy.
What Does Ozone Do to the Blood?
Ozone therapy increases the amount of oxygen in the blood, which helps to improve circulation, enhance immune function, and support detoxification. It may also help reduce the harmful effects of inflammation by neutralizing free radicals and promoting healing.
Conclusion
Ozone therapy, whether through insufflations, EBOO, or HD IV ozone, offers numerous potential health benefits. While it’s not yet approved by the FDA, the growing body of evidence supports its use for conditions ranging from chronic pain to autoimmune diseases. If you’re considering ozone therapy, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best method for your individual needs.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any new treatment.