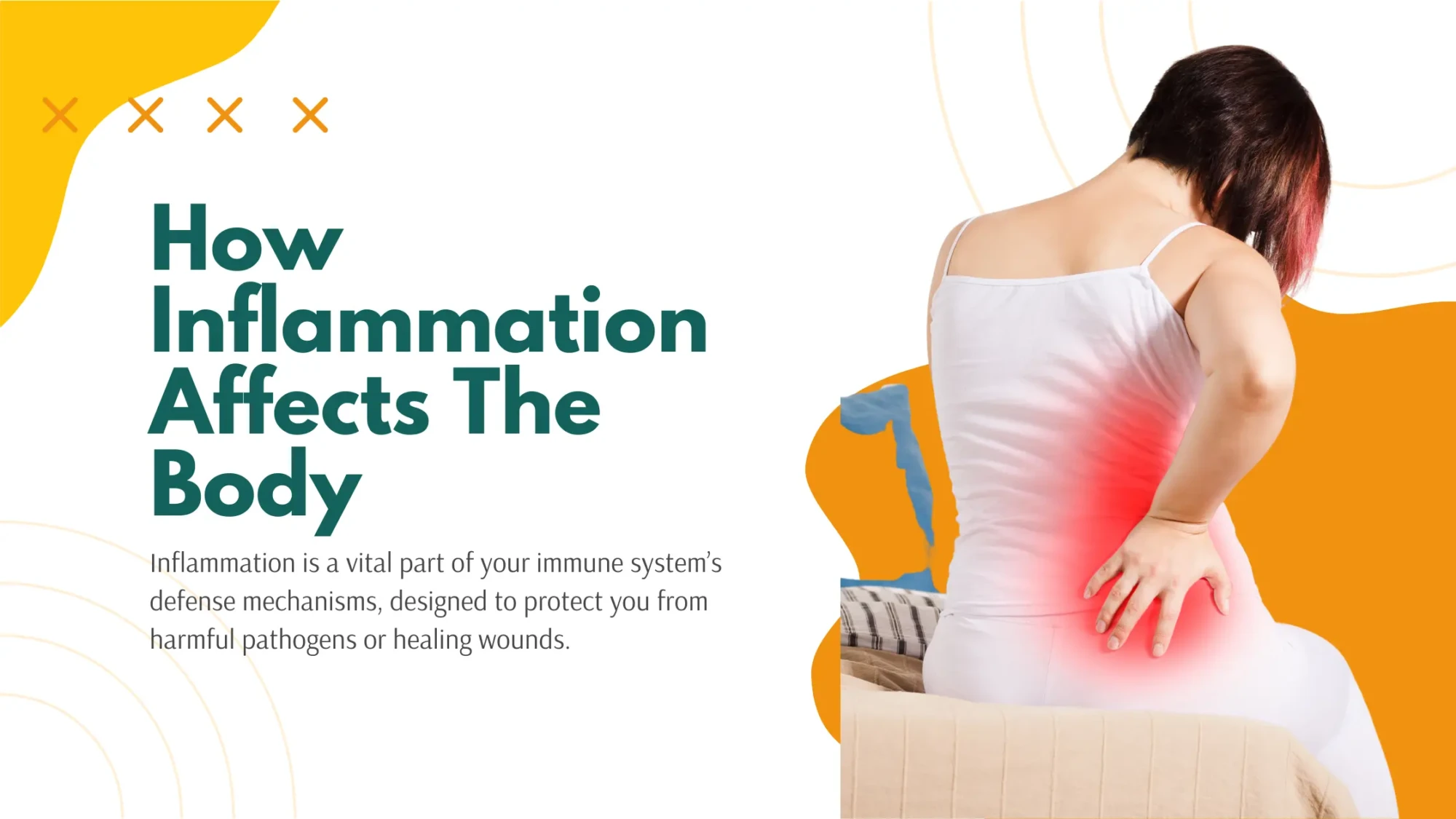
Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury or infection. It’s a vital part of your immune system’s defense mechanisms, designed to protect you from harmful pathogens or healing wounds. However, when inflammation becomes chronic or uncontrolled, it can lead to serious health problems. In this article, we’ll explore how inflammation affects the body, from …
Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury or infection. It’s a vital part of your immune system’s defense mechanisms, designed to protect you from harmful pathogens or healing wounds. However, when inflammation becomes chronic or uncontrolled, it can lead to serious health problems. In this article, we’ll explore how inflammation affects the body, from the ways it impacts various organs to how it contributes to long-term disease. We’ll also discuss practical ways to reduce inflammation and manage its impact on your health.
What Is Inflammation in the Body?
Inflammation is the body’s process of protecting and healing itself. When you experience injury, infection, or irritation, your body sends out inflammatory molecules like cytokines to the affected area. These molecules cause blood vessels to expand, bringing more blood—and more immune cells—to the area. This process helps fight infection and starts the healing process, but it can cause redness, heat, pain, and swelling.
While inflammation is generally helpful in the short term, it can become problematic if it persists over time. Chronic inflammation, in particular, can lead to serious conditions affecting various parts of the body.
How Inflammation Affects the Body
Inflammation can have a wide range of effects on different systems in the body. Although acute inflammation plays a key role in healing and fighting infections, chronic inflammation can damage tissues and organs over time. Here’s a deeper look at how inflammation affects the body:
How Chronic Inflammation Affects the Body
Chronic inflammation is a prolonged, low-grade inflammation that can last for months or even years. Unlike acute inflammation, which serves a protective role, chronic inflammation can harm the body. Here’s how chronic inflammation impacts various systems:
- Cardiovascular System: Chronic inflammation is a primary driver of heart disease. It can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, causing them to narrow and harden. This increases the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and high blood pressure.
- Immune System: Chronic inflammation can overwhelm the immune system, leading to autoimmune diseases. In these conditions, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues. Rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and type 1 diabetes are all linked to chronic inflammation.
- Digestive System: Chronic inflammation in the digestive system can result in conditions like Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and celiac disease. These diseases cause severe pain and long-term damage to the intestines.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Inflammation can disrupt the endocrine system, interfering with hormone production and regulation. For example, inflammation of the thyroid can cause hypothyroidism, a condition in which the thyroid doesn’t produce enough hormones.
- Brain and Cognitive Function: Prolonged inflammation in the brain is associated with cognitive decline and neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis (MS), and even autism. Inflammatory molecules known as cytokines can disrupt brain cell communication and affect memory and mood.
- Liver Function: Chronic inflammation in the liver can lead to fatty liver disease, liver fibrosis, and cirrhosis. This can impair the liver’s ability to detoxify the body and process nutrients properly.
How Does Inflammation Impact the Body?
Inflammation can affect the body in both acute and chronic phases. In the acute phase, inflammation helps to fight infections and heal injuries. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it starts to damage healthy cells, tissues, and organs. Over time, this damage can lead to a variety of health conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis.
- Tissue Damage: Chronic inflammation can destroy healthy tissues in various organs, including the joints, muscles, and digestive tract. This leads to pain, loss of function, and permanent damage.
- Organ Dysfunction: Inflammation can damage vital organs like the liver, kidneys, and heart. Chronic inflammation is a key contributor to conditions like fatty liver disease, kidney failure, and heart disease.
- Chronic Diseases: Long-term inflammation is a major cause of chronic diseases. For example, autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) all involve chronic inflammation.
How Does Brain Inflammation Affect the Body?
Brain inflammation, also known as neuroinflammation, can have serious effects on both the brain and the rest of the body. Neuroinflammation is linked to a variety of neurological and psychiatric conditions:
- Cognitive Decline: Chronic brain inflammation can impair cognitive functions, leading to memory loss, difficulty concentrating, and a decrease in overall mental clarity. This is particularly evident in conditions like Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
- Mood Disorders: Neuroinflammation has been associated with mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety. Inflammatory molecules in the brain can affect neurotransmitter function and alter mood regulation.
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: Conditions like multiple sclerosis (MS) and dementia are believed to be partly caused by inflammation in the brain. This inflammation disrupts nerve function, leading to disability and cognitive decline.
How Does Liver Inflammation Affect Body Weight?
How Inflammation Affects the Body: Liver inflammation is closely tied to metabolic health, including body weight regulation. Inflammation in the liver can lead to fatty liver disease, where fat accumulates in liver cells. This condition can interfere with the liver’s ability to process and store nutrients and regulate blood sugar. As a result, individuals with liver inflammation may experience difficulty losing weight or may even gain weight despite eating a healthy diet. Additionally, inflammation in the liver can lead to insulin resistance, a condition where the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin, increasing the risk of diabetes and contributing to weight gain.
Inflammation Affecting the Body’s Immune System
The immune system is designed to protect the body from harmful agents like bacteria, viruses, and toxins. However, chronic inflammation can have a paradoxical effect on the immune system. While it’s meant to protect the body, chronic inflammation can weaken the immune system by overstimulating it. This can lead to autoimmune diseases, where the immune system starts attacking healthy cells, tissues, and organs. Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis are examples of diseases caused by chronic inflammation.
How Does Inflammation Harm the Body?
When inflammation persists, it harms the body in several ways:
- Damage to Healthy Cells: Prolonged inflammation can damage healthy cells and tissues, leading to conditions like arthritis and chronic pain.
- Organ Dysfunction: Chronic inflammation can impair the function of organs such as the heart, liver, and kidneys. This can result in conditions like heart disease, liver failure, and kidney disease.
- Chronic Diseases: As mentioned earlier, inflammation is a key contributor to many chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders.
How to Reduce Inflammation in the Body
Reducing inflammation is essential for maintaining good health and preventing chronic disease. Here are some effective ways to reduce inflammation naturally:
- Anti-inflammatory Diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help reduce inflammation. Foods like berries, leafy greens, and fatty fish (like salmon) are particularly beneficial due to their high antioxidant content and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Regular Exercise: Moderate physical activity helps regulate the immune system and reduces inflammation. Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise most days of the week.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress is a known trigger for inflammation. Practices like meditation, yoga, and mindfulness can help reduce stress and inflammation.
- Adequate Sleep: Getting enough sleep is crucial for reducing inflammation. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to allow your body to repair itself.
- Supplements: Some supplements, such as turmeric (curcumin), omega-3 fatty acids, and ginger, have been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects. Always consult with a healthcare provider before taking new supplements.
What Happens If Inflammation Is Too High? How Inflammation Affects the Body
If inflammation remains elevated for long periods, it can cause significant damage to the body. Chronic inflammation is a key factor in the development of heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, and even some cancers. Over time, the damage caused by chronic inflammation can lead to organ failure, disability, and a decreased quality of life.
What Are the 5 Signs of Inflammation?
Here are the five classic signs of inflammation that you may notice in your body:
- Redness: Increased blood flow to the inflamed area causes redness.
- Heat: The inflamed area may feel warmer than usual due to increased blood circulation.
- Swelling: Fluid builds up in the tissues around the inflamed area, causing swelling.
- Pain: Inflammation can irritate nerve endings, leading to pain.
- Loss of Function: The affected area may lose its ability to function properly, such as difficulty moving a joint or trouble breathing.
What Is the Main Cause of Inflammation in the Body?
The main causes of inflammation include:
- Infections: Bacteria, viruses, and fungi can trigger inflammation.
- Injury: Physical injuries like cuts, sprains, or fractures cause inflammation as part of the healing process.
- Chronic Diseases: Conditions like obesity, diabetes, and autoimmune diseases can lead to chronic inflammation.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to toxins, pollutants, and allergens can promote inflammation.
- Diet: Poor diet, especially one high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats, can increase inflammation.
Chronic Inflammation Symptoms: How Inflammation Affects the Body
Symptoms of chronic inflammation can be subtle and include:
- Fatigue or feeling unusually tired
- Pain in the joints, muscles, or body
- Digestive problems, such as bloating or discomfort
- Frequent infections or slow healing of wounds
- Skin problems, including rashes or eczema
Conclusion
How Inflammation Affects the Body: Inflammation plays a crucial role in the body’s defense against infection and injury. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can lead to significant health problems, from heart disease to autoimmune disorders. By understanding how inflammation affects the body and taking steps to reduce it, you can protect your health and lower the risk of chronic diseases. Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet, managing stress, exercising regularly, and getting enough sleep are key strategies for keeping inflammation in check and promoting overall well-being.